Mobility is a cornerstone of independence, yet various diseases and disorders can significantly impact it. From the tremors of Parkinson’s to the joint pain of osteoarthritis, each condition presents unique challenges. Understanding these ailments is the first step toward effective management and improved quality of life.
Explore five such conditions that affect mobility.
1. Parkinson’s Disease: Impact on Movement and Coordination
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement. It’s characterized by tremors, stiffness, and bradykinesia, or slow movement. These symptoms result from the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. As the disease progresses, coordination and balance may also be impacted, making daily activities challenging.
Treatment options include medication, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery. Exercise and rehabilitation play a crucial role in managing symptoms and maintaining mobility. Support from healthcare professionals and caregivers is essential for individuals with Parkinson’s to navigate their condition effectively.
2. Multiple Sclerosis: Navigating Mobility Challenges
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system. It disrupts the flow of information within the brain and between the brain and body. Symptoms vary widely but often include fatigue, weakness, and difficulty with coordination and balance. These issues can lead to mobility challenges, making walking and daily activities more difficult.
Physical therapy and exercise are key components in managing MS-related mobility problems. Medications may also be prescribed to manage symptoms and slow disease progression. An assistive walking device can provide additional support for those with advanced mobility issues.
3. Stroke: Rebuilding Mobility and Independence
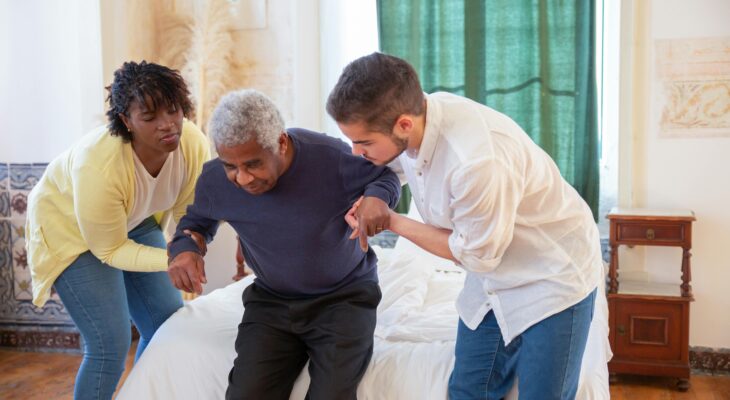
A stroke occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, preventing brain tissue from getting oxygen and nutrients. This can lead to paralysis, weakness, and coordination problems on one side of the body. Rehabilitation is crucial for stroke survivors, focusing on regaining strength, mobility, and independence.
Physical and occupational therapy play key roles in this process, helping individuals relearn movements and adapt to any remaining limitations. Assistive devices, such as walkers or wheelchairs, may be necessary for some individuals to enhance mobility and safety. With the right support and rehabilitation, many stroke survivors can make significant progress in regaining their mobility and independence.
4. Osteoarthritis: Managing Joint Pain and Mobility
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions worldwide. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones wears down over time. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility, particularly in the hips, knees, and hands. Managing osteoarthritis involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
A cane or walker, can provide additional support and stability for those with mobility challenges. Regular exercise and weight management are also crucial in reducing joint stress and improving overall mobility. With proper management, individuals with osteoarthritis can maintain an active and fulfilling life.
5. Spinal Cord Injury: Adapting to a New Normal
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is a life-altering event that can result in partial or complete loss of motor function and sensation. It often leads to paralysis, impacting mobility and independence. Rehabilitation is critical for individuals with SCI, focusing on maximizing remaining function and adapting to new ways of living.
Physical and occupational therapy play vital roles in this journey, helping individuals learn to navigate their environment with assistive devices such as wheelchairs. Advances in technology, such as exoskeletons, offer promising avenues for enhancing mobility. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and peers is essential for individuals with SCI to adapt to their new normal and lead fulfilling lives.
Wrap Up
Living with mobility challenges can be difficult, but it’s not insurmountable. Advances in treatment and rehabilitation offer hope and improvement. Embracing assistive devices and therapy can lead to significant strides in mobility and independence. Also, support from healthcare professionals and loved ones is crucial.